PhytoLab is a renowned ISO 17025-accredited testing laboratory and one of the world’s leading manufacturers of botanical reference substances. Our portfolio includes over 1,500 highly pure phyproof® reference standards – including numerous cannabinoids and cannabis terpenes. These substances are essential for qualitative and quantitative analysis of cannabis, especially in the quality control of medical cannabis, the breeding of new strains, and pharmacological research.

Cannabinoids & Cannabis Terpenes
Occurrence and Properties
Cannabinoids are biosynthesized in Cannabis sativa – a plant from the Cannabaceae family that has been cultivated for thousands of years as a medicinal and industrial crop. In addition to over 100 known phytocannabinoids, Cannabis sativa contains numerous other secondary plant metabolites such as terpenes, flavonoids, and nitrogen-containing compounds. The chemical composition varies significantly depending on the variety, cultivation, and processing. Reliable analytics therefore require validated and fully characterized reference standards – especially for pharmaceutical and forensic applications.
Regulatory Requirements and Research
Regulatory requirements for cannabis analysis have increased significantly in recent years. Since 01 July 2024, the new European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) monograph "Cannabis flower" has been in force. At the same time, terpenes are gaining increasing scientific interest in the context of the pharmacological effects of cannabis preparations – particularly in relation to the so-called entourage effect. This effect refers to specific combinations of cannabinoids and terpenes creating unique activity profiles. The composition and content of terpenes is strongly influenced by variety, cultivation, and processing – making precise terpene analysis indispensable for quality assurance and profiling.
Our phyproof® reference substance portfolio includes a wide range of cannabinoids and cannabis terpenes for standardized analysis. This includes mono-, tri-, and sesquiterpenes identified in Cannabis sativa, as well as specific markers for distinguishing synthetic cannabinoids, such as Olivetol and 4-Monobromocannabidiol . All substances are supplied with a detailed certificate of analysis (CoA).
| Substance | Product | CAS | Substance class | Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-)-α-Bisabolol | 80005 | 23089-26-1 | Sesquiterpenes | P |
| D,L-Camphene | 80063 | 79-92-5 | Monoterpenes | P |
| Cannabichromenic acid | 10017 | 185505-15-1 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabichromvarinic acid | 10047 | 64898-02-8 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabicitran | 22093 | 31508-71-1 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabidiol | 85705 | 13956-29-1 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabidiol hydroxyquinone | 10016 | 137252-25-6 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabidiolic acid | 85839 | 1244-58-2 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabidivarin | 85955 | 24274-48-4 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabigerol | 85956 | 25654-31-3 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabigerolic acid | 85958 | 25555-57-1 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabigerovarinic acid | 10018 | 64924-07-8 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabinol | 86068 | 521-35-7 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Cannabisin A | 86661 | 130508-46-2 | Amides | P |
| Cannabisin B | 86662 | 144506-17-2 | Amides | P |
| (+)-Δ-3-Carene | 80088 | 498-15-7 | Monoterpenes | P |
| β-Caryophyllene | 80717 | 87-44-5 | Sesquiterpenes | P |
| (-)-Caryophyllene oxide | 82496 | 1139-30-6 | Sesquiterpenes | P |
| p-Cymene | 80836 | 99-87-6 | Monoterpenes | P |
| Friedelin | 82543 | 559-74-0 | Triterpen sapogenines | P |
| α-Humulene | 83351 | 6753-98-6 | Sesquiterpenes | P |
| Linalool | 80885 | 78-70-6 | Monoterpenes | P |
| 4-Monobromcannabidiol | 10048 | 112639-10-8 | Cannabinoids | P |
| Olivetol | 10024 | 500-66-3 | Phenols | P |
| α-Pinene | 89257 | 80-56-8 | Monoterpenes | P |
| β-Pinene | 89335 | 127-91-3 | Monoterpenes | P |
| Sabinene | 82342 | 3387-41-5 | Monoterpenes | P |
| α-Terpineol | 89872 | 98-55-5 | Monoterpenes | P |
Structure
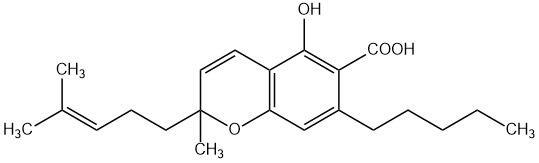
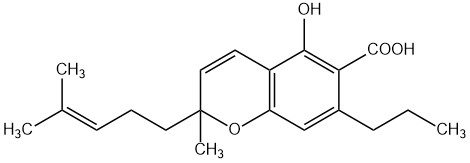
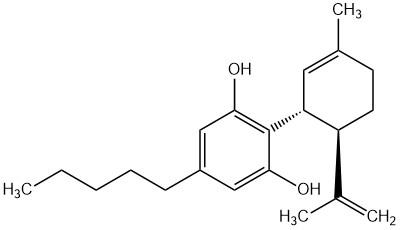
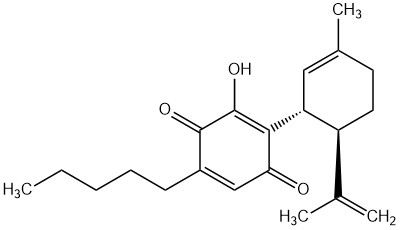
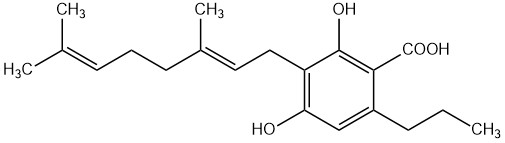
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the best-known non-psychoactive cannabinoid from Cannabis sativa. It plays a central role in medical research – especially for the treatment of pain, inflammation, and anxiety – as well as in the cosmetics industry. Due to its broad pharmacological profile, CBD is a key component of various formulations such as CBD oils or standardized cannabis extracts.

Conclusion
Reliable and reproducible cannabis analytics require fully characterized reference substances. Our cannabinoids and terpenes are supplied with comprehensive certificates of analysis – including quantitative determination of relevant residues such as Δ⁸-THC, Δ⁹-THC, and Δ⁹-THCA. In accordance with the DAC monograph "Cannabidiol", the limits have been set at 0.10% per single substance and 0.20% for the total.
👉 Detailed information on prices, specifications, and availability can be found on our product detail pages.